Note: we are republishing this story which originally made the news in March 2024.
A Texas mom sparked widespread disgust online after sharing her unsettling experience with what experts call "spaghetti meat" chicken. The viral post, which surfaced on X (formerly Twitter), has left many questioning the quality of poultry sold in stores.
Alesia Cooper, preparing dinner for her children, noticed something strange while washing chicken breasts purchased from Aldi. The meat began falling apart in her hands, turning stringy and squishy. “I think it’s fake meat,” Cooper wrote in her post, which quickly gained traction.
However, experts were quick to clarify the phenomenon. What Cooper encountered wasn’t “fake meat” but a condition known as spaghetti meat, which occasionally affects commercially farmed poultry.
Spaghetti meat is caused by modern breeding techniques designed to make chickens grow larger and faster. This rapid growth, particularly in breast muscles, can outpace the bird’s circulatory system, depriving muscle tissues of oxygen. As a result, the muscle fibers separate, creating a stringy texture reminiscent of spaghetti.

Photo Credit: Pexels
The National Chicken Council reports that chickens today grow at nearly twice the speed they did 50 years ago. In 1925, Chickens Took Over 100 Days to Reach Just 2.5 Pounds. By 2022, chickens reached 6.56 pounds in just 47 days. While this efficiency increases meat production, it also contributes to quality issues like spaghetti meat and a similar condition known as "woody breast," where the meat becomes tough and leathery.
Although the texture may be unappealing, experts assure consumers that spaghetti meat is still safe to eat, though it might be chewier than usual.

Photo Credit: Pexels
Cooper’s post, along with grim photos of the stringy meat, drew strong reactions. "I hesitated to share this, but if I had to see it, so do you," she wrote. The images sparked a mix of horror and curiosity among viewers, many of whom were unaware of the phenomenon.
Some fast-food chains and grocery stores, like Wendy’s and Whole Foods, are responding to consumer concerns. They’ve begun sourcing slower-grown chickens, arguing that these birds offer better texture and taste.
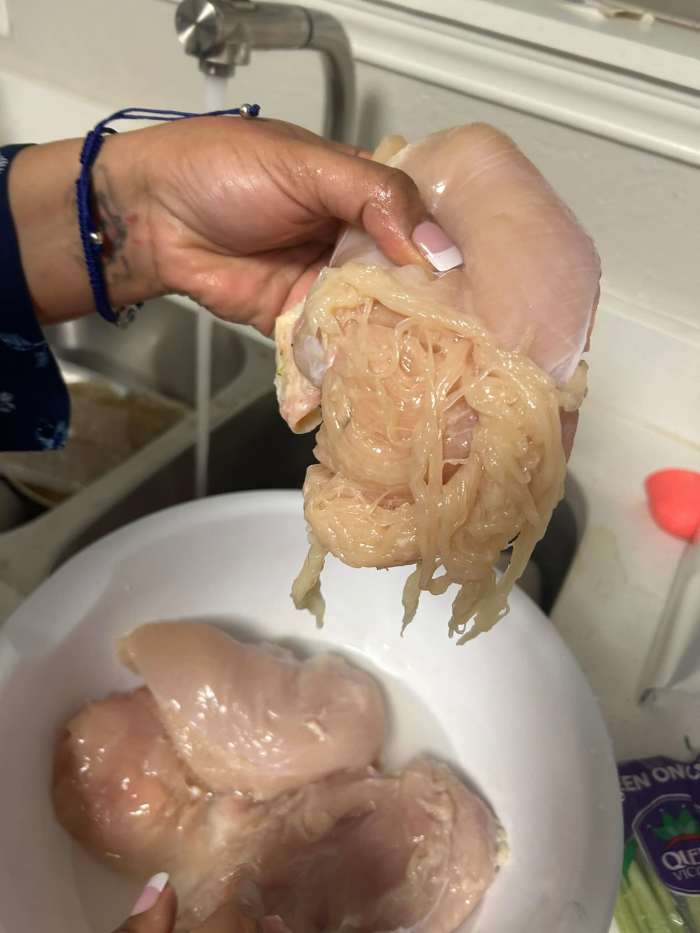
Photo Credit: Alesia Cooper/Facebook
According to Dr. Massimiliano Petracci, an agriculture and food science professor at the University of Bologna, fast-growing chickens are more prone to these abnormalities. Researchers first documented spaghetti meat in 2015, and by 2019, it was detected in 4-5% of chicken breast samples.
For many consumers, the discovery of spaghetti meat highlights the hidden consequences of modern farming practices—and why some are demanding higher standards in poultry production.
Sources: Daily Mail
